Arduino UNO wheel encoder: reads left/right ticks, provides counts, configurable ticks, wheel & pivot sizes, optional pose telemetry to ARC NMS.
How to add the Wheel Encoder Counter robot skill
- Load the most recent release of ARC (Get ARC).
- Press the Project tab from the top menu bar in ARC.
- Press Add Robot Skill from the button ribbon bar in ARC.
- Choose the Navigation category tab.
- Press the Wheel Encoder Counter icon to add the robot skill to your project.
Don't have a robot yet?
Follow the Getting Started Guide to build a robot and use the Wheel Encoder Counter robot skill.
How to use the Wheel Encoder Counter robot skill
This skill is compatible with Arduino UNO firmware that counts wheel rotation for left and right wheels.
Firmware
This robot skill requires supporting capability on the EZB with firmware. The firmware is open-source so that you can modify it for different Arduino's and microcontrollers. The Wheel Encoder Arduino UNO firmware can be found here: https://synthiam.com/Firmware/Wheel-Encoder-Firmware-NVXCXGPCQMJ
Main Window
1. Get Wheel Values Button Manually requests the encoder values for each wheel. Please do not use it when pushing to NMS because this is done automatically with an interval timer.
2. Reset Values Button Resets the encoder values back to zero. Please do not use it when pushing to NMS because it will break the current pose.
3. Get Wheel Values & Reset Button Resets the encoder values back to zero then starts acquiring the encoder values again. Please do not use it when pushing to NMS because this will break the pose.
4. Status Display When the debug checkbox is checked, this will display a text readout of the encoder values.
Configuration
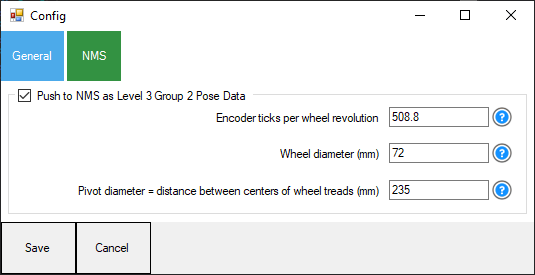
Settings - General
Poll Interval How often to poll the wheel encoder values from the Arduino.
Display debug information This will display the wheel encoder values to the log file for debugging in real-time.
Settings - NMS
Push to NMS Enabling this checkbox will push the data to the NMS as a Level 3 Group 2 sensor, updating the robot's positioning pose telemetry.
Encoder ticks per wheel revolution How many encoder ticks for one revolution of the wheel. This is used for the NMS pose calculation if enabled.
Wheel diameter (mm) The diameter of the wheel is in millimeters. This value must be precise because it is important to the pose calculation. If it is off by 1 mm, it will produce errors in the calculation. If you are using a known wheel product, use the datasheet to obtain the diameter. Otherwise, there are several methods to measure a wheel diameter. This is only used for the NMS pose calculation, if enabled.
Pivot diameter (mm) The distance between centers of wheel treads. Similar to the wheel diameter, this is absolutely important to be as accurate as possible. If using an existing robot product, consult the datasheet to obtain the pivot diameter, which is the distance between the center of each wheel tread. This value must be accurate and not have any errors. This is used for the NMS pose calculation.
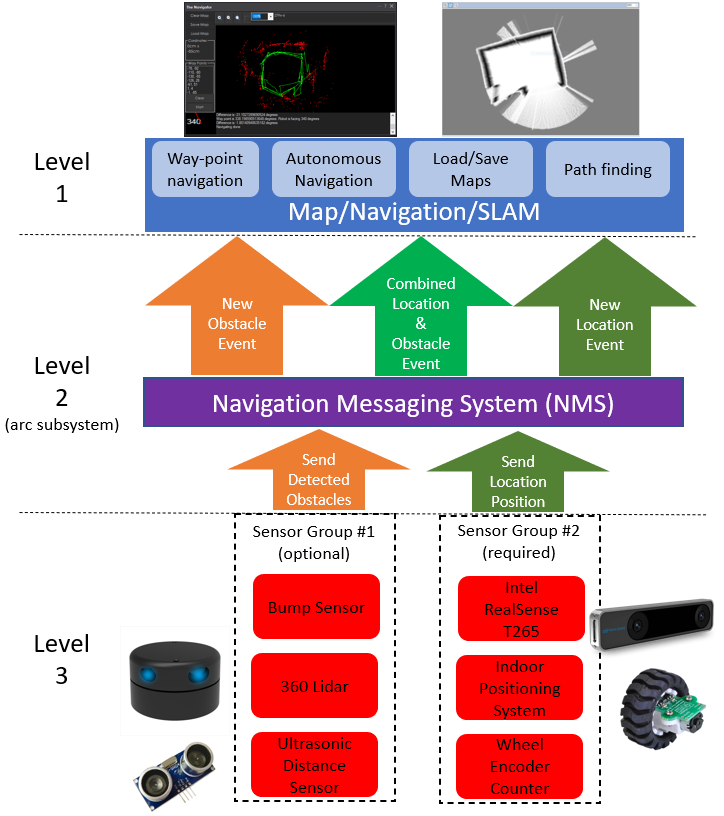
NMS
The Navigation Messaging System (NMS) is built into the ARC framework. It allows skills to push data (location & obstacle detection) into the messaging system. Then, mapping/navigation SLAM skills can subscribe to the navigation events. The NMS was designed to provide ARC users with transparent navigation. You do not have to write any complicated code because the robot skills will work for navigation and obstacle avoidance.How to Use Wheel Encoder Counter
Download the Arduino firmware onto a UNO (or edit for your Arduino version). The Wheel, Encoder Arduino UNO firmware, can be found here: https://synthiam.com/Docs/Hardware/Arduino-Genuino-Uno
Connect your wheel encoders to ports D2 (left wheel) and D3 (right wheel) on the UNO.
Add the Wheel Encoder Counter Skill (Project -> Add Skill -> Navigation -> Wheel Encoder Counter). Two script variables will now be created that hold each wheel's encoder values, respectively ($LeftWheelCount & $RightWheelCount). Or, you can enable the NMS checkbox in the configuration settings to push the pose to NMS as a Level 3 Group 1 sensor.
Connect the UNO to ARC.
Video
Resources
The Wheel Encoder Arduino UNO firmware can be found here: https://synthiam.com/Firmware/Wheel-Encoder-Firmware-NVXCXGPCQMJ
There is a ControlCommand() to reset the $LeftWheelCount and $RightWheelCount values or force-get the values on demand rather than automatically on a timer. Do not reset or manually poll the wheel count using the NMS because it will affect the current pose data.
You can see how this skill was created by watching the live hack event here: synthiam.com/HackEvent/Dj-s-5th-Live-Hack-Session-17578
Control Commands for the Wheel Encoder Counter robot skill
There are Control Commands available for this robot skill which allows the skill to be controlled programmatically from scripts or other robot skills. These commands enable you to automate actions, respond to sensor inputs, and integrate the robot skill with other systems or custom interfaces. If you're new to the concept of Control Commands, we have a comprehensive manual available here that explains how to use them, provides examples to get you started and make the most of this powerful feature.
Control Command ManualcontrolCommand("Wheel Encoder Counter", "GetValues") Query the EZB firmware and get the latest encoder values. Set the values to the NMS (if checked) and populate the global variables.
controlCommand("Wheel Encoder Counter", "GetValuesAndReset") Query the EZB firmware and get the latest encoder values. Set the values to the NMS (if checked) and populate the global variables, and reset the values to zero.
controlCommand("Wheel Encoder Counter", "ResetValues") Reset the counter values to zero.
Related Hack Events
Related Questions
What Is Really Needed For Indoor Navigation?
Arduino EZB Firmware To ARC Communication

Converting Motor To Digital Signal
Upgrade to ARC Pro
ARC Pro is your gateway to a community of like-minded robot enthusiasts and professionals, all united by a passion for advanced robot programming.
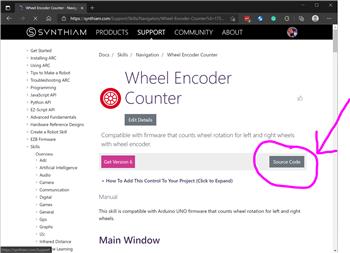
 Source Code
Source Code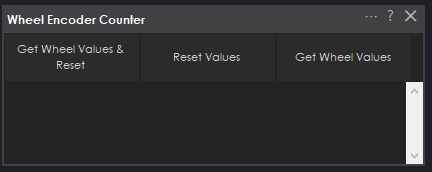


8400 counts is the wheel turning 1 complete rotation. 4200 counts is the wheel turning half a rotation.
If your wheel radius of your wheel is 10cm, then 8400 counts would be 10 cm of travel.
16800 counts would be 20cm of travel
Some questions on this skill. Won't you need an A and B output for when it goes backwards? Won't you need to select the comport for the Arduino to have it get it's data. Maybe it's built into this skill for two encoders (could not find it) but how about when you have many encoders? I hooked up a typical encoder's A to D2 of the Arduino, 5v, gnd, B was not wired into anything and rotated the encoder by hand but did not get any changing values in the variables. Have a feeling that it needs to have the comport selected within the skill itself.
You would need to read the description of this robot skill again. It's an extension of an EZB firmware. It IS built into the firmware. The Movement Panel knows which direction the encoder is going. Although many encoders have two wires, this would benefit from supporting those types as well. You could update it for that.
Have the comport scenario figured out. Is there an update for 2 wire encoders-did not see it. Tried the encoder skill as it is now connecting properly but it gave me this feedback. "the connected device does not support the required capability to count wheel encoding. Using an Uno so would think it would have been fine.
You do not have the correct firmware. Please read the manual and follow the instructions. There’s too much for me to repeat here. Please read the manuals before posting.
Updated to require v2 of the EZB Firmware found here: https://synthiam.com/Firmware/Wheel-Encoder-Firmware-NVXCXGPCQMJ
Updated to require v3 of the EZB firmware from here: https://synthiam.com/Firmware/Wheel-Encoder-Firmware-NVXCXGPCQMJ