Navigation Messaging System
The Navigation Messaging System (NMS) is built into the ARC framework. It allows skills to push data (location & obstacle detection) into the messaging system. Then, mapping/navigation SLAM skills can subscribe to the navigation events. The NMS was designed to provide transparent Navigation to the user in ARC. You do not have to write any complicated code because the robot skills will work for navigation and obstacle avoidance.
NMS Stack
The NMS stack consists of sensors that feed the messaging system, received by mapping skills.
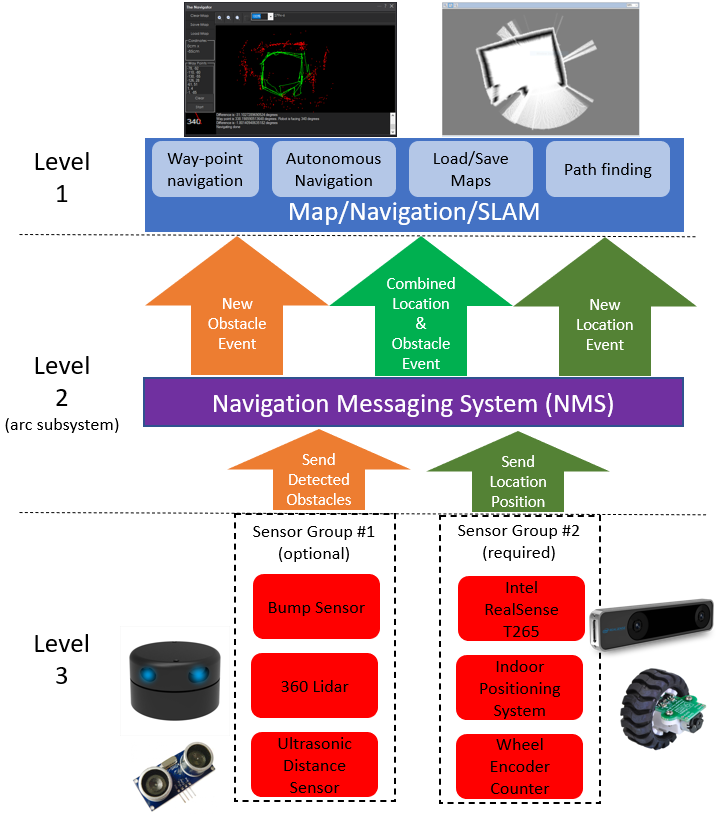
Level #1 - Map & Navigation
This is how to view the sensor data and organize it into maps for navigating. There are a few skills that do this. They subscribe to the sensor event data and assemble a map. Then, they allow you to click on the map and instruct the robot where to navigate to (either way-point or any destination, depending on your sensor data). A few navigation skills are...
-
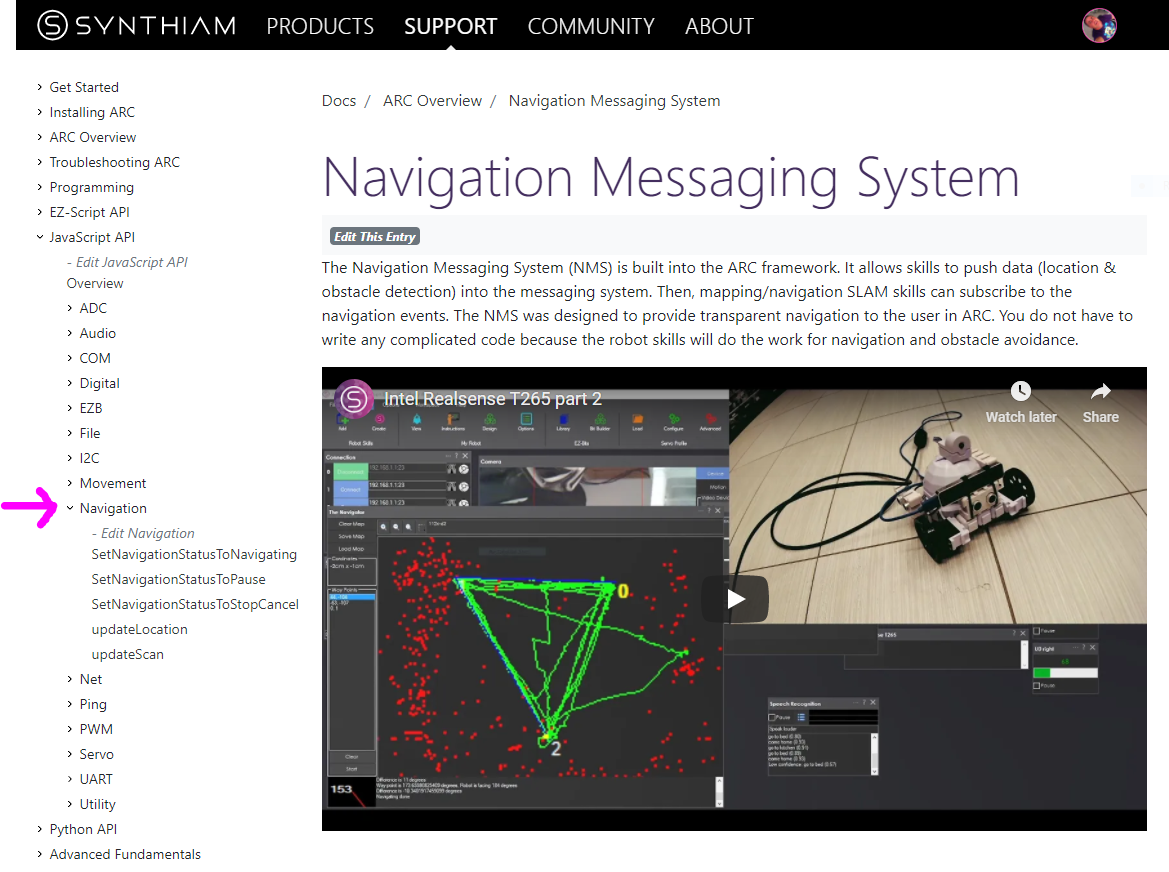
(preferred)The Better Navigator by SynthiamBetter Navigator Hector SLAM-based NMS navigation that maps with LiDAR/depth, saves waypoints, plans paths and avoids obstacles for autonomous travelRequires ARC v42
-
The Navigator by SynthiamPath-planning navigator using ARC NMS position and obstacle data to map, log trajectories, and autonomously follow waypoints.Requires ARC v31
-
EZ-SLAM by SynthiamCreates a map in a global variable; proof-of-concept SLAM visualizer (very experimental).Requires ARC v25
Level #3 - Sensor Groups
You require sensors that feed data into the messaging system that maps are made from. The navigation messaging system collects data by supporting two sensor input groups...
-
Lidar/depth scanners: any sensor that can detect obstacles (laser, 360-degree lidar ultrasonic, IR, etc.). The sensor will detect objects and mark on the map where the robot cannot go (i.e., walls, sofa, chairs, etc.). Supported skills are...
-
Intel Realsense D435i by IntelConnect Intel RealSense depth cameras to ARC NMS for depth-based distance detection, point-cloud mapping, video streaming, and navigation telemetry.Requires ARC v20
-
Hitachi-LG LDS Lidar by HitachiHitachi-LG 360° LiDAR driver that feeds scans into ARC's Navigation Messaging System for obstacle detection, SLAM mapping, and navigation integrationRequires ARC v21
-
Ultrasonic Distance by SynthiamDisplays HC-SR04 ultrasonic distance readings in ARC; scriptable via GetPing(), pausable, sets a variable with multiplier, optional NMS output
-
Kinect Xbox 360 Depth Mapping by MicrosoftPublishes Kinect (Xbox 360) obstacle distance scans to ARC NMS for SLAM/Navigator, using configurable detection area to ignore irrelevant depth.Requires ARC v3
-
Rplidar by SlamtecSlamtec LiDAR driver that streams 360° scans to ARC NMS (Level 3, Group 1) for SLAM, mapping, and navigation with offset and COM configuration.Requires ARC v27
- JavaScript & Python commands for manually reporting obstacle detection
-
-
Localization telemetry pose navigation:
Special sensors that keep track of the robot's position (pose) in the real world (IPS, wheel encoders, Roomba movement panel, intel realsense t265, etc.). *Note: only one Group #2 sensor can be active at one time.
-
Intel Realsense T265 by IntelT265 VSLAM for ARC: SLAM-based mapping and precise way-point navigation, low-power tracking, and NMS telemetry.Requires ARC v26
-
Indoor Positioning System by SynthiamInfrared indoor positioning for ARC robots: dual-camera tracks IR beacon, shows real-time heading, path and EZ-Script navigation variablesRequires ARC v16
-
Wheel Encoder Counter by SynthiamArduino UNO wheel encoder: reads left/right ticks, provides counts, configurable ticks, wheel & pivot sizes, optional pose telemetry to ARC NMS.Requires ARC v13
-
Irobot Roomba Movement Panel by iRobotControl Roomba/Create via ARC: drive, stream sensors, read encoders, configure COM/HW UART, and send pose to NMS for mapping/navigation.Requires ARC v22
-
NMS Faux Odometry by SynthiamEstimate pose odometry from movement distance for robots without encoders, calibrated by speed. Suited for DIY navigation; pose drifts with lidar.Requires ARC v8
-
Camera NMS Pose by Synthiam Inc.Overhead camera tracks a glyph to give precise robot pose to ARC's NMS for multi-camera indoor/outdoor navigation and waypoint controlRequires ARC v8
- JavaScript & Python commands for reporting positioning manually
-
What Sensors Do You Need?
Depending on what NMS Level 1 mapping/navigation you will be using, the sensor requirements may differ. For example, using the mapping skill
Scripting Support
NMS commands are supported by the JavaScript and Python scripting compilers in ARC. The namespace is Navigation, and You can view more details in the Support section for JavaScript or Python. The script commands allow custom sending Level #3 Group #1/#2 sensor data into the NMS. As well as pausing and stopping any ongoing navigation by a Level #1 navigator.
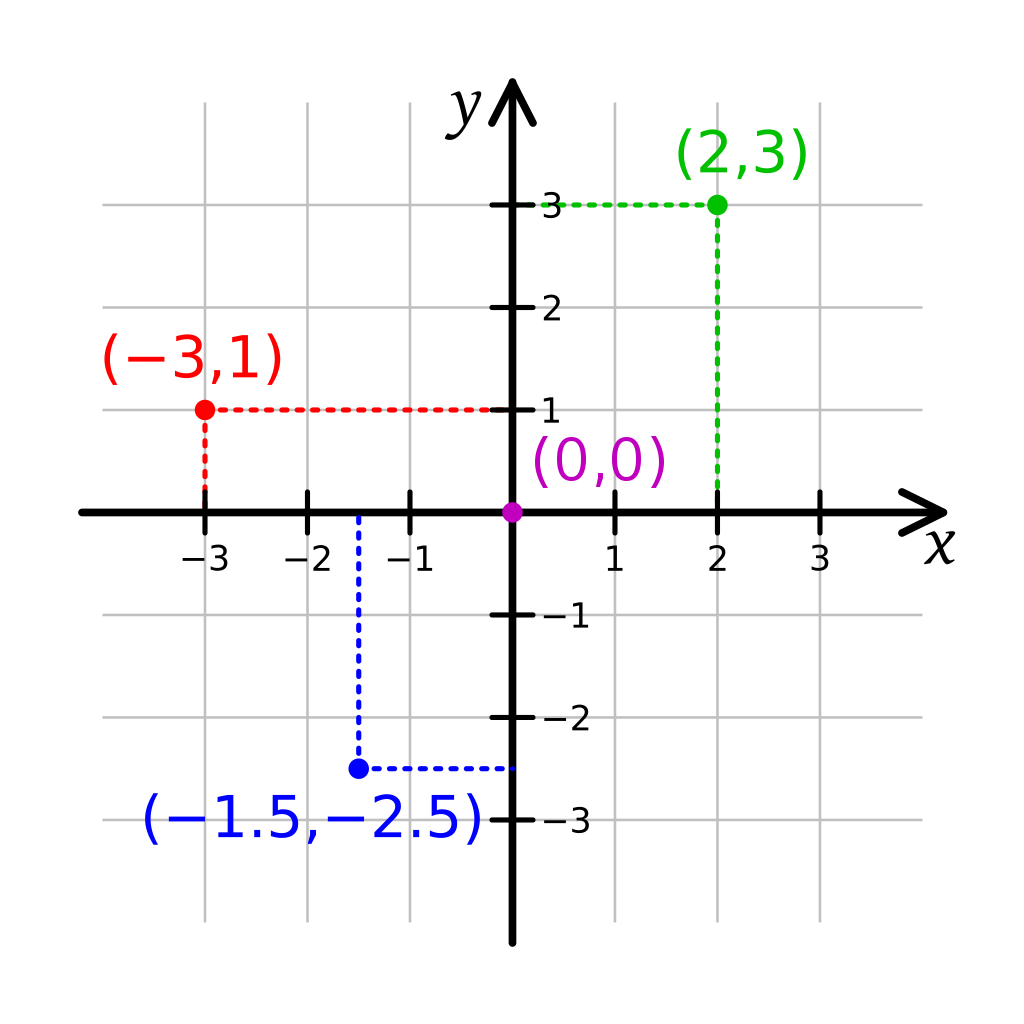
Cartesian Coordinate System
This robot skill uses cartesian coordinates to reference the robot's starting position. The starting position is always 0,0 and is defined at startup. As the robot navigates, the skill measures the distance from the starting position. The unit of measurement is in CM (centimeters). Read more about the cartesian coordinate system on Wikipedia.
Further Reading
Many experts have researched and documented robotics's navigation, localization, and known pose positioning. While the Intel T265 has demonstrated the most significant success at inside-out localization, many other methods have been attempted over the years. The topic of reach into robot navigation is far too vast to be covered in this manual. However, we'll leave you with a few papers that have greatly influenced the robot industry in this field.
- Where Am I? - Systems and Methods for Mobile Robot Positioning by J. Borenstein, H. R. Everett, and L. Feng
- Carleton Winter 2012 Position Estimation presentation
All Navigation Robot Skills
These are navigation robot skills that work with the NMS or assist with controlling the robot's movement.