Movement Panels
A Movement Panel is a type of robot skill responsible for moving the robot in directions (forward, left, right, stop, reverse, etc.). A movement panel robot skill integrates with the ARC environment and allows other controls or scripts to instruct the robot to move in any direction. When a movement panel is added to your project, it registers itself as the responsible control for directional movements. ARC has many movement panels. For example, there are HBridges, Continuous Rotation Servos, Auto Position GAITs, AR Parrot Drones, and iRobot Roombas.
An advantage of a Movement Panel is that you do not need to code logic for the robot hardware to move. Instead, use movement commands with the optional speed parameter to have the movement panel respond automatically. That will instruct the Movement Panel to do its thing, even for an H-bridge, drone, gait, etc...
The advantage of using movement panels is agnostic robot hardware per project. Consider if you built a robot that performs a specific task using an H-bridge movement panel. You can replace the hbridge Movement Panel with any other movement panel (such as a drone or Auto Position for Hexapod or humanoid).
Any project can interchange any movement panel with any other movement panel. The advantage of using movement panels is not to require code for a specific hardware configuration, thus allowing agnostic hardware configurations per project.
Contents
- Project With Movement Panel
- Directions
- Speed
- Scripting
- Speech Recognition
- Other Robot Skills
- Camera Control
- User Interface Builder
- Programming and Variables
- RoboScratch
- Blockly
- Create Custom Movement Panel
Project With Movement Panel
This screenshot is of a robot project that contains a movement panel. All other robot skills can send commands to the movement panel to control the robot. For example, with a checkbox in the camera device, the robot can follow a ball for any movement panel and any robot type. The same code can be used for a different robot hardware configuration by swapping the movement panel with another.

Directions
The ARC framework provides several pre-programmed directions: forward, left, right, reverse, stop, roll right, roll left, up, down, and custom. Movement panels will support the directions that are appropriate to their movement type. For example, an HBridge movement panel will not support UP or DOWN because the robot must have wheels and cannot fly. You can see what directions are supported on a movement panel by the buttons visible on the interface. This diagram demonstrates how the various directions are expected to behave by movement panels. For example, turning left or right will likely rotate on the spot. However, turning slightly right while moving forward will require the robot to move forward with the right wheel speed somewhat slower than the left.
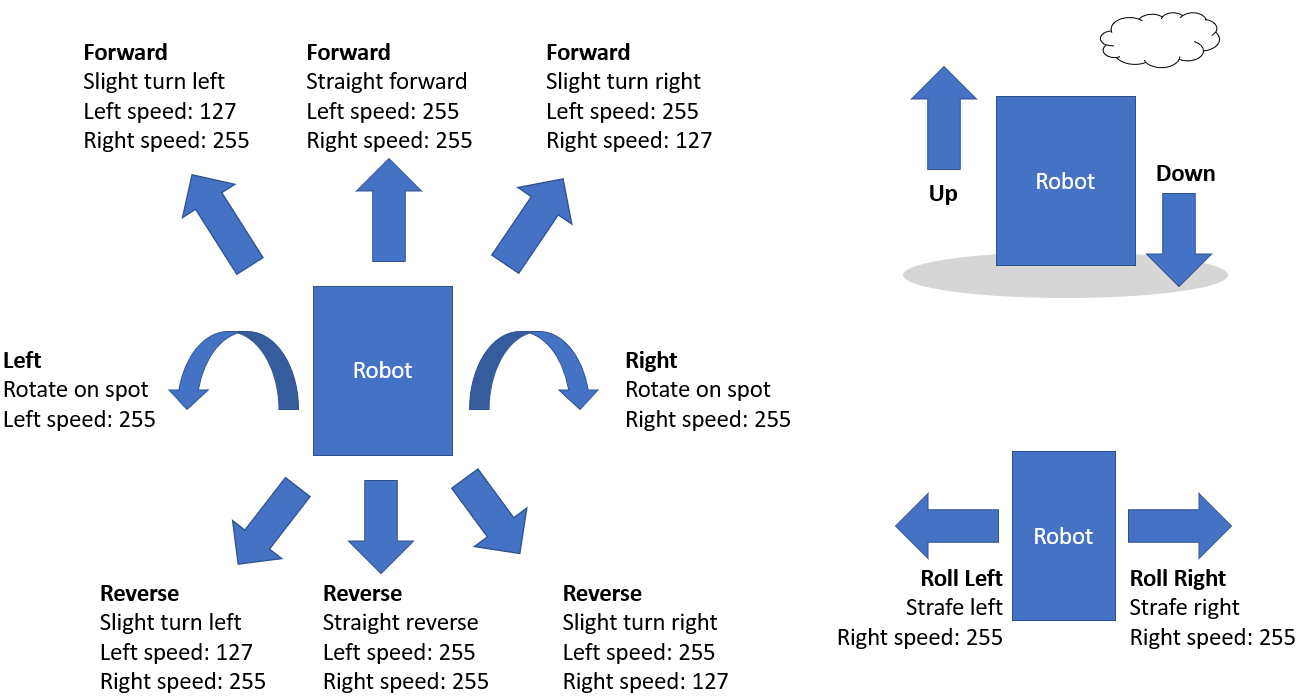
Speed
When specifying a direction to move, most movement panels will support a speed range between 0-255. The left and right wheels can have different speeds for driving forward with slight arc turns in either direction. This allows joysticks and tracking skills to control the robot's movement better.
Scripting
When a Movement Panel is added and configured in your project, documented scripting commands will instruct the movement panel to begin moving the robot. If, anywhere in your project, you executed the script command Forward(), the script engine will instruct the project's Movement Panel to begin moving forward. It is recommended to reference the script manually in ARC for the desired language. Click HERE for the manual of your preferred scripting language.
Speech Recognition
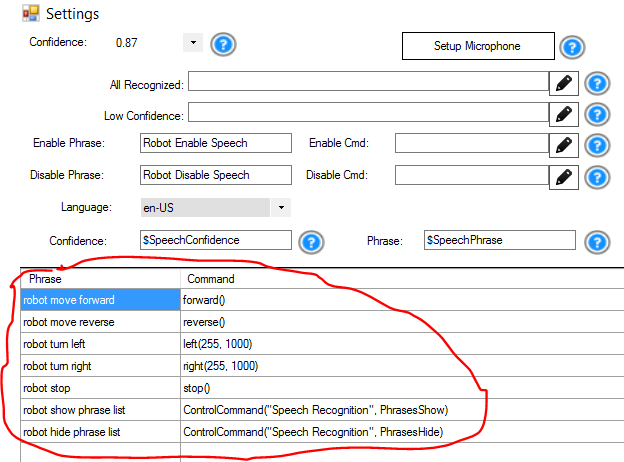
Some controls, such as the Speech Recognition Control, will trigger scripts based on user input (speech). The default configuration of the Speech Recognition Control includes speech commands and respective scripts for instructing the Movement Panel to move the robot. Viewing the Speech Recognition configuration, you will see script direction commands...
Other Robot Skills
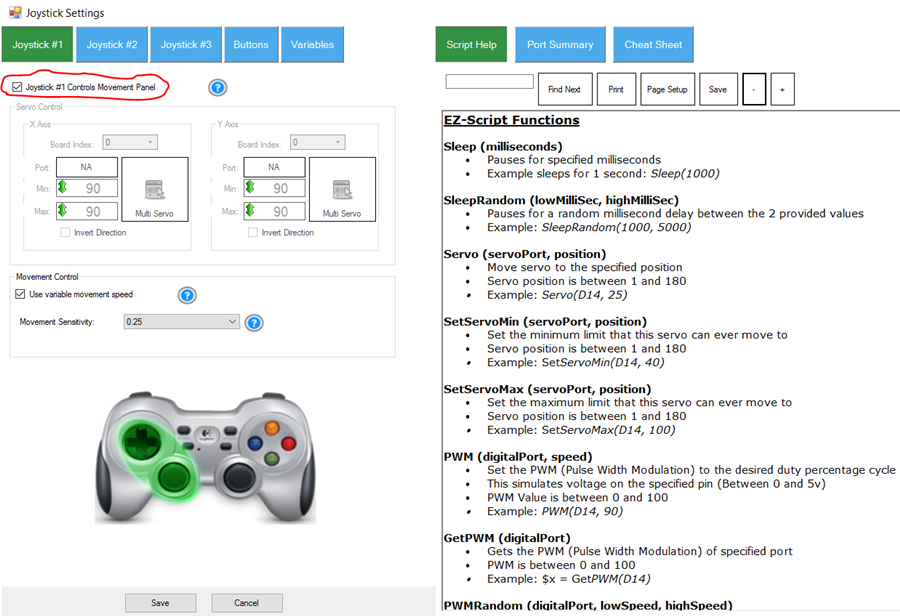
Good question! Now that we know how the script can instruct a movement panel to move, how do other controls work with movement panels? Well, that's the magic of ARC. For example, if a Joystick Control was added to your project, pushing forward on the joystick will instruct the Movement Panel to begin moving forward. The Joystick control is pre-configured to send the Forward command to ARC. The registered Movement Panel will respond to the direction request. Let us take a look at the settings menu for Joystick Control. Here you will see the checkbox which assigns Joystick #1 to the "Control Movement Panel."
Camera Control
Yes! The camera control has an option in the settings to instruct Movement Panels to move in any direction based on the tracking method configured. The tracking method is how the robot will respond to tracking a specific tracking type. You can learn more about camera control and terminology by clicking HERE. If the Camera Control is configured to follow an object with MOVEMENT, it will instruct the current Movement Panel. Let's take a look at the Camera Settings and where the option is to have the camera control a movement panel.
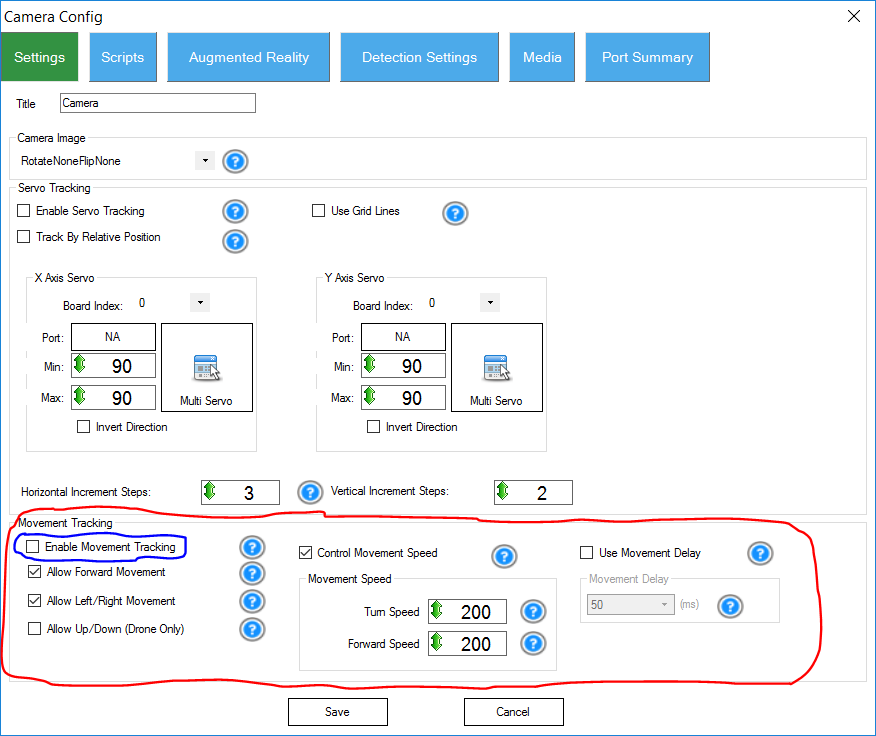
*Note: Highlighted in RED is the section that contains options to configure how the Camera Control will communicate with the Movement Panel. Highlighted in BLUE is the checkbox which turns on/off the ability of the Camera Control to track movement. There are blue question marks that provide more information.
User Interface Builder
The trend in this lesson is that any control or script dealing with movement will instruct the current Movement Panel to move the robot in the specified direction. This also applies to widgets within the User Interface Builder. Within the User Interface Builder, you may add buttons to control movement direction with script commands (Forward(), Left(), Stop(), etc.). Or, you may add the Joystick Pad.
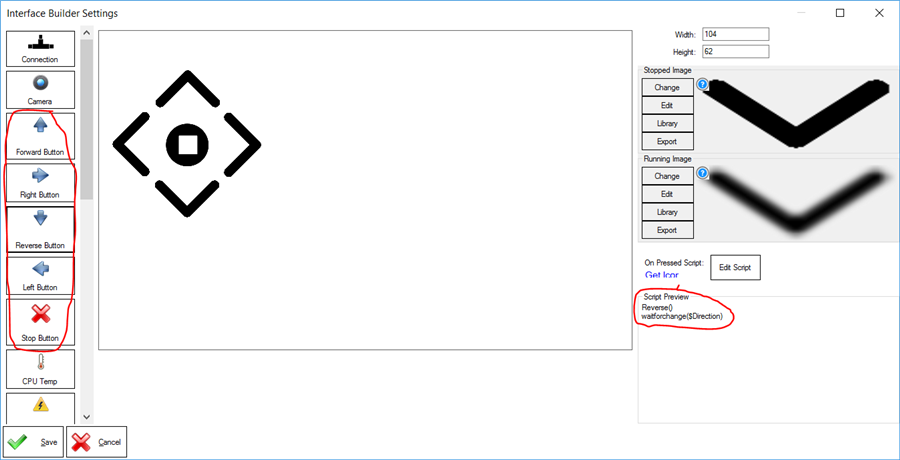
Here is an example of buttons added to the User Interface Builder, which will instruct movement using script commands (Forward(), Left(), Stop(), Right(), Reverse(), etc.).
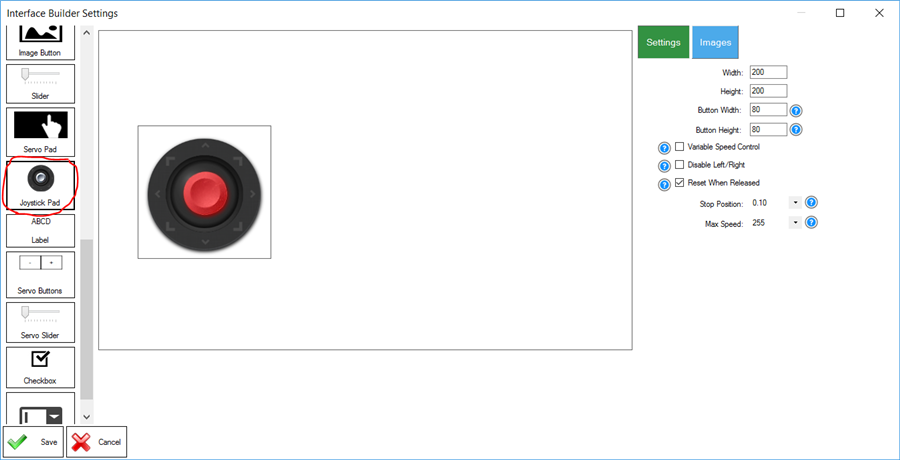
Here is an example of using the Joystick Pad in the User Interface Builder, which automatically instructs the Movement Panel. One advantage to the user interface builder's Joystick Pad is that it can control the speed of the movement panel supports it.
*Note: You can tell if a movement panel supports speed because it has a speed slider.
Programming and Variables
The current direction and speed of the robot's movement are accessible in scripting as global variables. Custom scripts can use these variables to know the direction or speed of movement. Or the variables are also used when creating a custom movement panel to understand the user-selected direction and speed. You can see the global variables if you add one of the variable watcher robot skills. The global $DIRECTION variable can determine the current direction. To choose how to access global variables, check the manual for the programming language that you're using. ARC can use different programming languages and access the global variable storage. For example, if using JavaScript, you can get the current direction with the getVar() command.
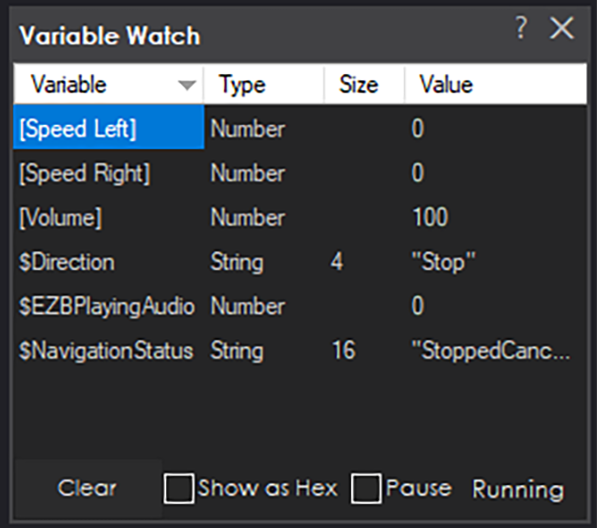
The current speed can also be obtained using the respective GetSpeed commands for your selected programming language. For example, if using JavaScript, you can get the left wheel speed with the GetSpeedLeft() command.
Now, we've covered getting the data from the movement, but you can also set the direction and speed of movement. This can be done using the movement commands and setSpeed commands. Again, you must check the manual for the specific programming language you're using with ARC.
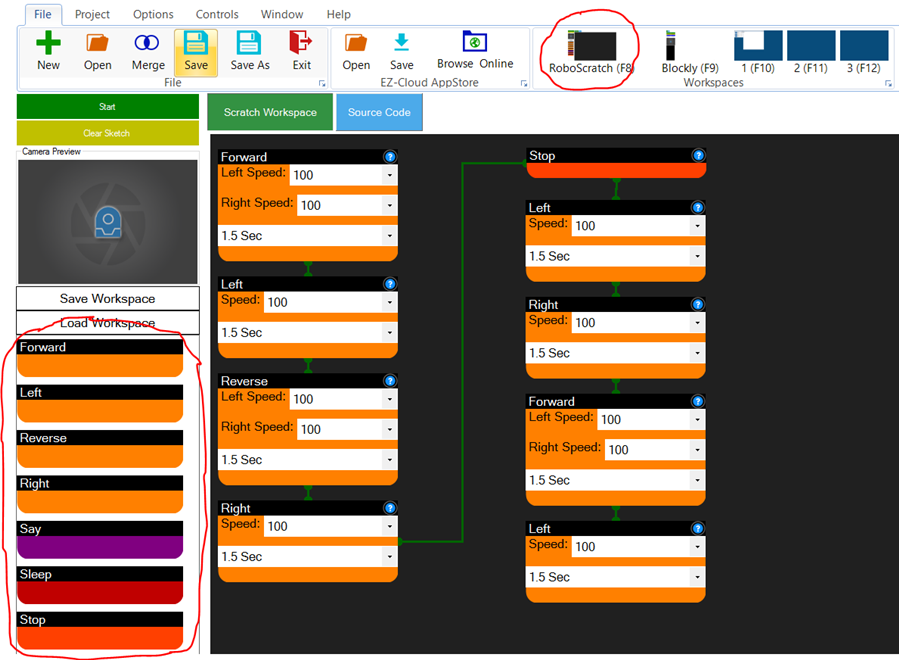
RoboScratch
Any reference to moving (Forward, Left, Right, Stop, etc.) will automatically instruct the project's current Movement Panel to begin moving. This includes using either RoboScratch, an excellent beginning programming interface with ARC.
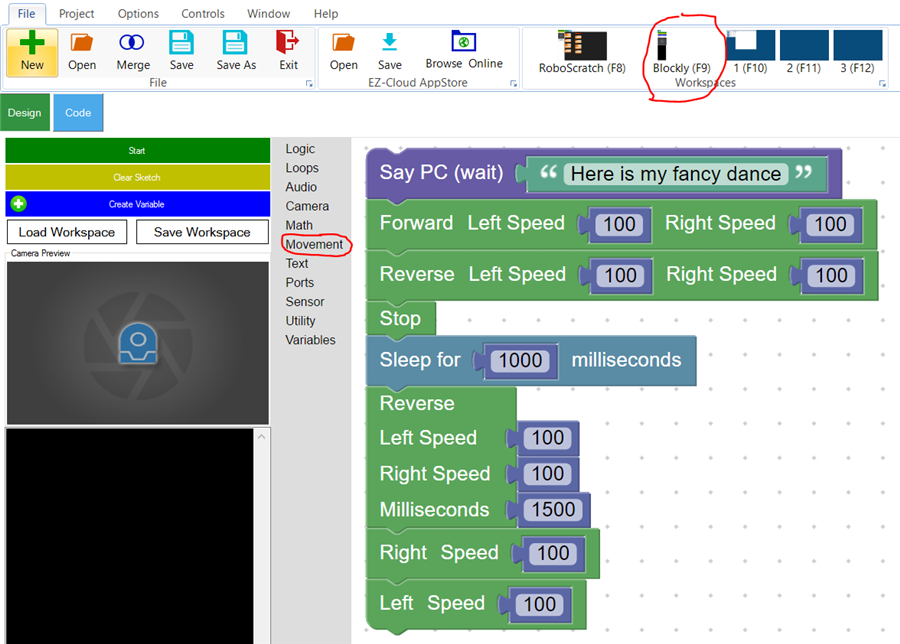
Blockly
Any reference to moving (Forward, Left, Right, Stop, etc.) will automatically instruct the project's current Movement Panel to begin moving. This also includes using Blockly, an excellent intermediate programming interface with ARC.
Create Custom Movement Panel
As mentioned earlier, ARC has many movement panels for HBridges, Continuous Rotation Servos, Auto Position GAITs, and even AR Parrot Drones or iRobot Roombas. However, if you seek to create a custom movement panel, the Custom Movement Panel is what you are looking for. The Custom Movement panel contains events for each direction (Forward, Left, Right, Stop, Reverse) for which you may add custom code.
ARC will execute the event in the Custom Movement Panel when another control requests to move your robot (i.e., forward, left, right, stop, reverse). Yes, the joystick will control your custom movement panel. Yes, the camera will send commands to your custom movement panel. The point of this document is that any mention of a movement in ARC will instruct the movement panel to move the robot, even a custom movement panel.