
Esp32 Devkit V1 by Espressif
Firmware
The DOIT ESP32 DevKit v1 is an affordable Wi-Fi controller with plenty of I/O and three hardware UARTs. With the firmware below installed, the board behaves like an EZB that Synthiam ARC can connect to over Wi-Fi. This firmware is compatible with ARC 2019.06.25.00 and newer.
2, 4, 12–19, 21–23, 25–27, 32–33.
Video Tutorial
Wi-Fi Modes
The firmware supports two Wi-Fi modes:
- AP Mode – the ESP32 creates its own Wi-Fi network and acts as the server that ARC connects to.
- Client Mode – the ESP32 joins your existing Wi-Fi network (router), and ARC connects to the ESP32’s IP address on that network.
You can view the current IP address and connection status using the Arduino IDE
Serial Monitor set to 115200 baud.
Port Configuration
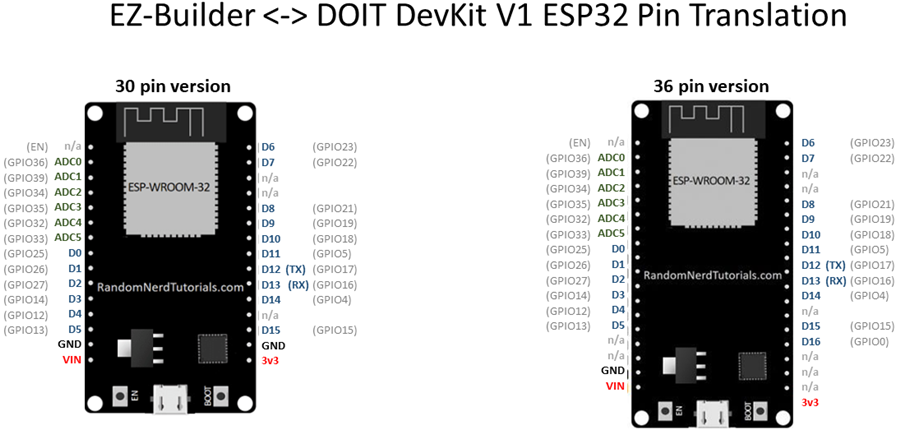
In ARC, the digital ports are labeled D0–D23. On the ESP32, the pins are labeled with GPIO numbers that are not in sequential order. Use the pin translation diagram below to map ESP32 GPIO pins to ARC Dx ports.
Pins marked TX/RX are the hardware UART pins and correspond to hardware UART #0 in ARC.

I wouldn't bother with the adafruit servo controller because the communication is slow and a little wonky with i2c.
You'd get more out of an Arduino with a servo shield. Simply connect the Arduino's RX and TX to the TX and RX of the ESP32 cam.
Once you do that, the firmware change is minor on the esp32. All you need to do is a while () loop that passes TCP to the UART and vice versa. All of the EZB code is removed.
Here, this is how it would work: https://synthiam.com/Firmware/ESP32-Cam-Arduino-Relay-XFXISYJTEYQ
To compile on Arduino IDE 2.0.3 I had to change line 591 to: analogWrite(translateaDigitalPort(port), (uint16_t) map(pos, 0, 100, 0, 255));
I'm assuming here it is supposed to use the included analogWrite and not the Arduino included one?
I don't think an Arduino analog write exists for the ESP Arduino library. At least at the time of the firmware creation, there wasn't. It shouldn't matter which one you use if there happens to be an Arduino AnalogWrite installed with the ESP package.
But i think you need to be casting the value to a uint8_t not a uint16_t. Because it's only a byte from 0-255. I mean, the 16bit int will work but it's unneeded extra bits
Gotcha. I commented out analogWrite and moved the files out of the project and it compiled. Looks like it was included November 2021 since version 2.0.1 so after the firmware was written.
esp32/hardware/esp32/2.0.6/cores/esp32/esp32-hal.h:void analogWrite(uint8_t pin, int value);
Aside from that error the rest of the firmware compiled fine.
that's good to know - i might have to revisit that firmware and remove the analogwrite.h to use the built-in one.
so you got it working then?
Yeah I'm just sitting at my bench with multimeter testing the PWM's on the pins. Works great.
p.s. nabu'er here as well :-) actually that's how I found ARC. It's just a hobby of mine and learning ros2 was not fitting into my schedule anytime soon.
I was really impressed how well the ESP32 worked with ARC. I think if someone sat down and built a free 3D printed opensource series of robots like a robot humanoid, robot hexapod, robot car etc based on the ESP and called it something like ES-Robot, it would be a huge success for schools and hobbyists