Diagnose EZ-B connection reliability by stressing UART, ADC, digital, voltage, temp and audio; detects disconnects, data errors, and flaky hardware.
How to add the EZB Stress Test robot skill
- Load the most recent release of ARC (Get ARC).
- Press the Project tab from the top menu bar in ARC.
- Press Add Robot Skill from the button ribbon bar in ARC.
- Choose the General category tab.
- Press the EZB Stress Test icon to add the robot skill to your project.
Don't have a robot yet?
Follow the Getting Started Guide to build a robot and use the EZB Stress Test robot skill.
How to use the EZB Stress Test robot skill
Synthiam robots rely on external embedded controllers such as the EZ-Robot EZ-B v4 to interface with sensors, motors, servos, ADC inputs, audio devices, UARTs, and digital pins.
These connections may be wireless (Wi-Fi/TCP/IP) or wired (USB/UART) - and depending on noise, signal quality, device placement, power stability, workload, or firmware behaviour, communication may degrade over time. In field deployments, instability can result in:
- Unexpected disconnects
- Delayed command processing
- Lost sensor values
- Audio failures
- Telemetry gaps
- Inconsistent I/O readings
url=/uploads/user/DB763BE15E695777689418BE7364E0A3/c3ld3yd0.png]
The EZB Connection Stress Test robot skill is used to identify, reproduce, and diagnose these issues by placing a continuous, repeatable workload on the EZ-B communication layer. It confirms whether an EZ-B controller remains stable and responsive under sustained traffic.
This tool is useful both during development and before deployment to verify system stability.
1. How to get started
This robot skill should be added to an empty project. It is not recommended to mix this robot skill with existing skills because that adds extra details which could affect the test results.
- In an empty project, add this robot skill to ARC.
- Connect to the EZBs that you wish to test.
- Select the ENABLE checkbox on the robot skill.
- Check the test types that you wish to test. Read about each test below in their own section. Ensure the type of test is supported by your EZB. For example, Arduinos do not have audio capability and some may not have UART capability.
- Let the test run for 24 hours or longer if needed.
2. What the Skill Does
When activated, the skill:
- Detects the number of EZ-Bs that are connected at the moment testing begins.
- Executes selected test operations in a continuous loop.
- Validates correctness by comparing expected results with actual responses.
- Records total executions of each test type.
- Stops automatically if a failure, disconnection, unexpected connection event, or corrupted response occurs.
All outcomes are written to the log for review or technical analysis.
3. Typical Use Cases
- Verifying robot reliability before live operation or competition
- Diagnosing intermittent connection issues
- Stress-testing new or repaired systems
- Identifying defective cables or signal integrity issues
- Validating Wi-Fi signal quality in different physical environments
- Characterizing stability when multiple EZ-Bs are active
- Troubleshooting unexplained audio, voltage, sensor, or serial failures
This skill often reveals faults that do not appear under light usage but surface under continuous load.
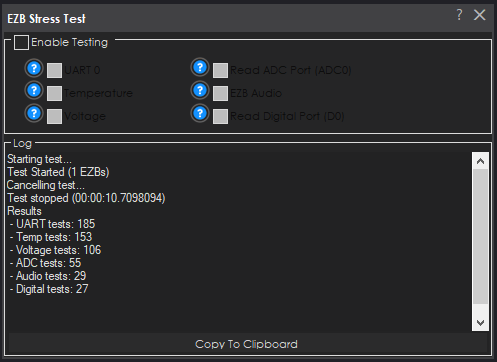
4. Interface Overview
Enable Test
The primary on/off control. When checked, testing begins against all currently connected EZ-Bs. When unchecked, the test is cancelled.
The skill automatically unchecks this box if a failure occurs, ensuring the operator is notified when testing halts unexpectedly.
Test Type Selection
The interface contains multiple checkboxes allowing the operator to choose which operations are exercised during stress testing:
- UART loopback testing
- CPU temperature reads
- Battery voltage measurement
- ADC reading
- Audio note synthesis
- Digital input reading
Multiple tests may be enabled simultaneously, which increases load and better simulates real usage conditions.
Copy Log
Copies the entire diagnostic output log to the clipboard for reporting, documentation, or support inquiry.
5. Test Descriptions and Diagnostic Value
5.1 UART Loopback Test
This test verifies serial transport reliability by writing a string through UART channel 0 and immediately reading it back.
If any byte differs, or if the response length does not match the sent length, the communication path is considered unstable.
Loopback Wiring Requirement
For the UART test to function, TX and RX on UART0 must be physically connected together so that transmissions return to the receiver.
Procedure:
- Locate UART0 TX and RX pins on the EZ-B.
- Insert a jumper wire between the TX pin and RX pin.
- No other wiring is required.
If TX and RX are not bridged, the test will fail because no echo is received. If the jumper is installed but returned data is corrupted or incomplete, this indicates true signal degradation, noise, or hardware fault.
This makes the UART loopback test a highly effective indicator of cabling quality, grounding issues, connector reliability, or serial adapter malfunction.
5.2 Temperature Request Test
Repeatedly requests CPU temperature values from the EZ-B controller. This verifies:
- The EZ-B can accept and respond to telemetry requests
- The command pipeline is not starved or blocked
- The controller does not stall under repeated polling
5.3 Battery Voltage Measurement Test
Reads the internal battery voltage value. This test is designed to confirm:
- ADC stability
- Conversion integrity
- Responsiveness under load
Voltage readings that degrade during extended testing can be an early warning of power supply instability or regulator issues.
5.4 ADC Input Test
Queries ADC channel 0 for a value. Even if no analog signal is attached, the act of reading ensures that ADC request and response handling remains functional under prolonged usage.
Failures often correlate with firmware starvation or unstable signal paths.
5.5 Audio Synthesizer Test
Commands the EZ-B to generate a short musical note. This validates:
- Command initiation
- Internal timing paths
- Audio subsystem responsiveness under communication load
Audio commands are timing-sensitive, making this an effective stress probe.
5.6 Digital Input Test
Reads a state value from digital port D0. This verifies:
- Digital bus accessibility
- Firmware handling of continuous I/O requests
Digital I/O failures often indicate compiler or firmware priority issues.
6. Test Behavior and Failure Conditions
The test repeats continuously until one of the following occurs:
- The operator disables the test
- The cancellation token is triggered
- A communication error is detected
- An EZ-B disconnects or a new one attaches
- Data returned does not match expected values
When a problem is detected, the test:
- Stops immediately
- Displays an error message
- Unchecks the Enable box
- Prints a detailed statistics summary
This provides an immediate and unambiguous failure signature.
7. Multi-EZB Behavior
This skill intentionally enforces a fixed device set:
- Number of EZ-Bs at test start is recorded.
- If the count changes, testing aborts.
This helps detect:
- Wi-Fi dropout
- TCP routing issues
- AP density problems
- High-load packet loss
- Intermittent supply voltage collapse
Multi-EZB installations are especially susceptible to bandwidth contention, and this diagnostic mechanism helps reveal such conditions.
8. Best Practice Guidelines
- Run tests for extended periods (1 to 48 hours) to identify latent failures.
- Use proper UART jumpers when testing serial reliability.
- Test multiple environments (robot lab, field deployment, different buildings).
- Start with one enabled test type, then gradually add more to increase stress.
- Repeat after firmware changes, hardware adjustments, or cabling modifications.
- Perform tests before mission-critical deployment.
9. Result Interpretation
No failures
Indicates stable communication and subsystem responsiveness.
UART failures
Almost always related to wiring or electrical characteristics. Check jumper quality, power grounding, cable length, and noise sources.
Sporadic failure in one subsystem only
Suggests firmware starvation within that subsystem. Audio failures under load are especially telling.
Disconnects
Likely power instability, router congestion, or RF environment issues.
Failure only with multiple EZ-Bs
Usually bandwidth or routing conflict. Consider AP channel adjustments and load balancing.
10. Logging and Supportability
The log includes:
- Time stamp of test start
- Error details
- Loop execution counts per subsystem
The Copy Log button enables easy export for:
- Manufacturer support requests
- Engineering debug review
- Integration documentation
The EZB Connection Stress Test robot skill is not a runtime automation tool; it is a diagnostic and qualification instrument.
Its value lies in exposing weaknesses in communication, electrical stability, firmware state handling, and carrier integrity before they cause unpredictable robot behaviour.
Using this skill during development, installation, commissioning, or maintenance materially reduces field failures and improves long-term reliability of robotic systems built using the EZ-B v4 controller.