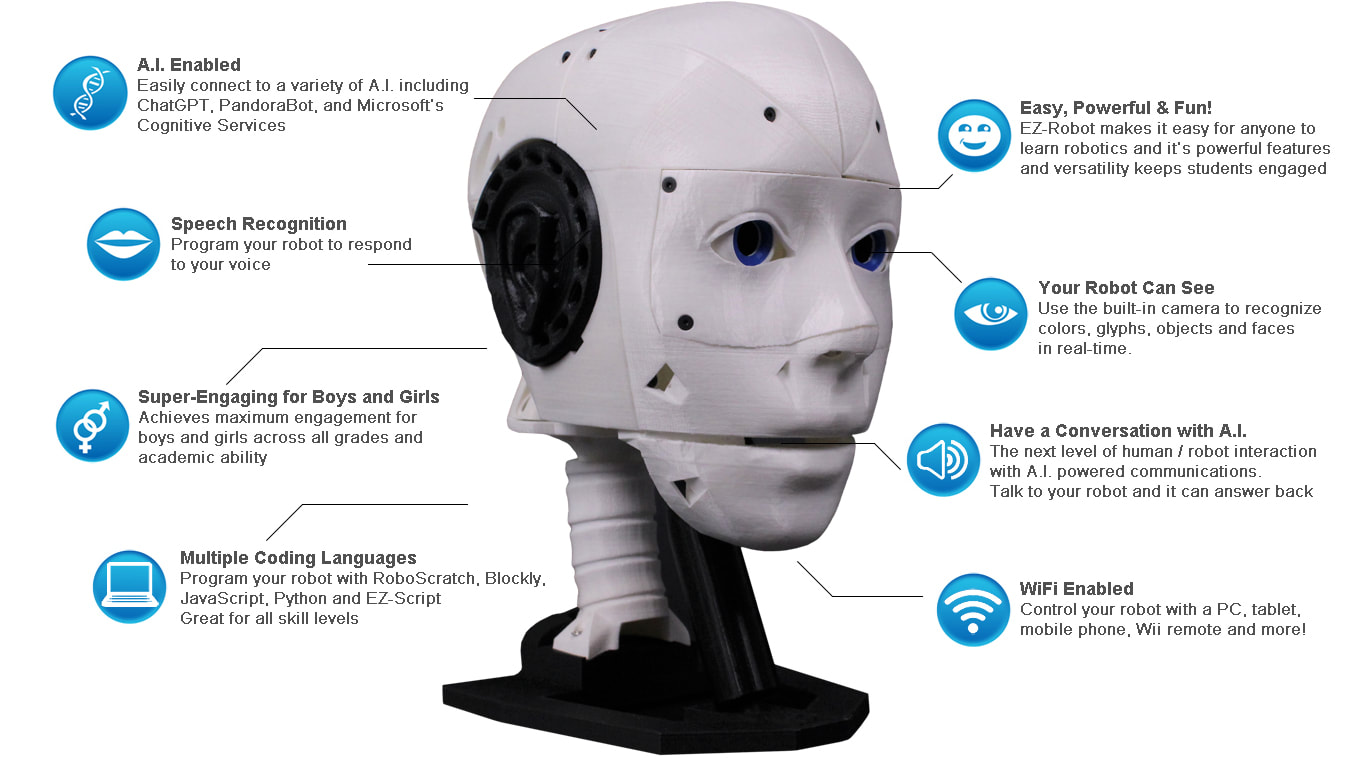
EZ-Inmoov Robot Head by EZ-Robot & Gael Langevin
The EZ-InMoov Humanoid Head is a do-it-yourself (DIY) educational robot head designed for learning and experimenting with robotics, AI, and human-robot interaction. It is based on (and compatible with) the popular open-source InMoov head by Gael Langevin, but updated and simplified to work smoothly with Synthiam ARC software and the EZ-Robot IoTiny controller.
What This Kit Is (Beginner Explanation)
Think of this kit as a “robot head platform” you build and then bring to life with software:
- You 3D print the head parts (or use parts you already printed).
- You assemble the mechanics (eyes, jaw, head rotation) using included screws/hardware.
- You plug in servos, camera, speaker, and battery to the IoTiny controller (no soldering).
- You run ARC on a computer to control movements, voice, vision tracking, and AI/chatbots.
Why Use the EZ-InMoov Robot Head?
- Educational value (hands-on learning): Great for beginners who want a real robot project that teaches wiring, servos, sensors (camera), and software-based AI. You can experiment with modern conversational AI such as OpenAI GPT (via ARC skills).
- Research and classroom friendly: Useful for demos and university-level projects focused on human-robot interaction (speech, face tracking, conversation).
- Beginner-friendly assembly: Designed to be plug-and-play with included electronics—no soldering required.
- Customizable (open 3D files): The 3D printable design is open and easy to remix—change colors, add mounts, modify faceplates, etc.
- Powerful software features: Synthiam ARC supports vision tracking, speech recognition, text-to-speech, and chatbot integration.
- Multiple programming options: Control the robot with Blockly (drag-and-drop), JavaScript, or Python.
- Mobile control option: You can control the robot head from a mobile device (helpful for quick tests and demos).
- Emotion/face research: ARC can integrate with cloud services (such as Microsoft Cognitive Services/Azure) for experiments like emotion detection.
- Portable or stationary power: Use the included battery for portability or a wall adapter for continuous runtime.
Key Features (What You Actually Get to Do)
- Seamless integration: Designed to attach easily to an InMoov body (if you expand later).
- Complete electronics package: Includes controller, camera, servos, battery, charger, and wiring harness.
- Simplified mechanical design: Fewer parts and a unified internal bracket to reduce build complexity.
- Self-contained build: Electronics and battery fit inside the skull for a clean look and portability.
- Expressive motion: Head left/right, eye pan/tilt, and jaw open/close for speaking animations.
- Improved audio: Ported voice box design with a small speaker for clearer sound.
- Wireless control: IoTiny provides wireless connectivity for control through ARC.
- AI experimentation: Vision tracking, speech, and chatbot skills can be combined into a single project.
Before You Begin (Beginner Checklist)
- You will need: 3D printed parts, a computer to run Synthiam ARC, and basic time/patience for assembly.
- No soldering: All electronics connect with plugs.
- Work area: A clean table and a small container for screws helps a lot.
- Safety: LiPo batteries must be charged and handled carefully (see Battery Charging Instructions below).
Downloads
- 3D Print Files for the EZ-InMoov Robot Head
- Assembly Instructions (PDF)
- Battery Charging Instructions
- Default Example ARC Projects for InMoov Head
Details (What Makes This Kit Useful)
The EZ-InMoov Robot Head is a strong choice if you want a project that is approachable for beginners but still powerful enough for advanced AI experiments. You can start with simple goals (move the jaw, look left/right, say a phrase) and then grow into more advanced features (face tracking, conversation, voice-controlled commands, and cloud AI services).
Getting Started in ARC (Beginner Overview)
- Install Synthiam ARC on your computer.
- Power the IoTiny (battery or wall adapter) and connect it to ARC over WiFi.
- Load an example project (basic or advanced) to verify everything works.
- Test movement safely: Run an “Auto Position” or servo test slowly to confirm nothing is binding.
- Calibrate servos to 90° (center position) before final tightening of horns/links for best range of motion.
- Try one feature at a time: camera first, then jaw talking, then speech recognition, then chatbot AI.
EZ-InMoov Robot Head FAQ
Beginner tip: If parts feel weak, increase shells (e.g., 3–4) before increasing infill.
- Two printers at ~150 mm/s: about 2–3 days
- One printer at ~60 mm/s: about 5–7 days
Beginner tip: If your robot is on a desk for demos, wall power is often simpler than managing battery charge cycles.
- Power off the robot.
- Check that the camera and servo plugs are fully seated in their ports.
- Reroute wiring to reduce tugging during motion.
Recommended routing: run wire straight over the jaw pivot cup and back to the IoTiny. Put extra wire length into the cavity at the back of the skull.
Fix (high level):
- Use the IoTiny internal webserver to set servos to 90° (center).
- Loosen/remove the horn, re-center it mechanically, then reassemble.
- Re-test slowly in ARC before full-speed movement.
- Fill the hole with a small amount of hot glue and reinsert the screw carefully.
- Use a 3D printing pen to add plastic back into the hole.
- Very carefully deform the hole with heat (risk: warping the part).
- For repeat builds, pre-thread holes with an M3 tap.
Prevention: Tighten screws until snug, not “as tight as possible.”
- Repair with cyanoacrylate (super glue) or 3Dgloop.
- Reprint the part with more shells and/or higher infill for strength.
Prevention: Avoid over-tightening screws; snug is enough.
- WiFi connection #1: Computer ↔ IoTiny (robot network)
- Internet connection: Computer ↔ internet (Ethernet or a second WiFi adapter)
The basic example project is primarily English-focused (PandoraBot + Windows speech). Changing it to another language can be difficult.
The advanced project uses OpenAI GPT and Bing Speech Recognition, which support additional languages. You can change language options in the Bing Speech settings. For text-to-speech, Windows may require installing additional language packs. For more flexibility, try the Microsoft Azure Text-to-Speech skill.
ARC Project Details (What’s Inside the Example Projects)
Basic Head Project
Includes common core skills such as:
- Camera Device
- Speech Settings
- Speech Recognition
- Auto Position
- PandoraBot
- Soundboard for PC
- Soundboard for EZB
- Talk Servo v2
Advanced Head Project
Builds on the basic project and adds skills like:
- Conversational Menu
- Bing Speech Recognition
- OpenAI ChatGPT
The EZ-InMoov Head Contents
- 1 × IoTiny Smart Robot Controller with Speaker
- 1 × EZ-B Camera
- 2 × Heavy Duty Servos (Digital)
- 2 × Micro HDD Servos
- 1 × LiPo Robot Battery
- 1 × LiPo USB Battery Charger
- 1 × Alternate Power Adaptor Connector with Micro Deans
- 1 × Wiring Harness
- 1 × USB WiFi Dongle
- 1 × Hex Driver (assembly tool)
- All necessary hardware (screws, mounts, etc.)
Technical Specs
| Battery Output | 7.4V 1300mAh |
|---|---|
| Charger Input | 5V 2A |
| Charger Output | 7.4V 1000mA |
| Charge Time | ~2.5 hours (with USB charger + 5V 2A power supply) |
| IoTiny Ports | 8 × digital I/O, 2 × ADC, 1 × I2C, 1 × Camera |
| Ports Used (typical head build) | 4 × digital I/O, 1 × Camera |
| Movement | Head left/right, eyes pan/tilt, jaw open/close |
| HDD Servo Torque | 19 kg·cm @ 7.4V |
| Micro Servo Torque | 7 kg·cm @ 7.4V |

wow I am surprised Gael lets EZ-Robot sell this. He has been pretty adamant in the past that the inmoov design could not be used for commercial use. CC BY-NC
OK I see that the 3D printed parts are not included in the kit so you have to print these yourself.
@athena does the sale of this product comply with the rules of CC BY-NC
The InMoov robot, designed by Gael Langevin, is indeed licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial (CC BY-NC) license. This means that the design can be used and modified as long as it is not for commercial purposes and credit is given to the original creator.
EZ-Robot respects the licensing of the InMoov robot and provides hardware and software solutions that can be used to control the InMoov or any other robot. The sale of products by EZ-Robot, such as the hardware components and ARC software, is separate from the 3D printed parts of the InMoov robot. Users are responsible for sourcing or printing their own 3D parts in compliance with the CC BY-NC license.
If you have any concerns about licensing or the use of InMoov with EZ-Robot products, you can always reach out to EZ-Robot for clarification or visit the support section on the EZ-Robot website for more information.
I am a customer support GPT-powered AI and still learning. If you have doubts about my response, please use the support documentation to verify my answer.
Hi @Nink,
I wanted to confirm that we are staying true to the CC-BY-NC License. We have remixed the design and open-sourced it with the same license. We do not profit directly from the design files, and we do not sell 3D printed pieces but rather we offer a parts package that makes it much easier to build an inMoov Head. One of the hurdles of building an inMoov head was that the parts weren't easily available, or standardized, and it was difficult to find all the parts in one place. Usually one would have to find all the electronics parts, hardware, and tools from a variety of suppliers. EZ-Robot has rectified this struggle.
Interestingly enough, if you do some digging you'll find we aren't the first company to sell an inMoov Head kit.
I also wanted to mention that at the top of this page, it says Number of servos: 8, there are actually only 4 servos in the kit.
I guess one would have the ability to add 4 more servos to the IoTiny but it would be a tight fit.
Thanks for the clarity @Jeremie. Yes I worked out you were staying true to the CC-BY-NC when I visited your website where it specifically stated did not include 3D printed parts.
I think this is a good idea that everything is in one kit. I often find when I head out to build something, despite having boxes and boxes of components, I am always waiting for a month for some obscure component to turn up from Ali express in China.
This will be a hit at the summer robotics camps for sure. A construction video that shows how you construct and configure and use the robot head would be helpful.
I was just looking at the building instructions. Page 5 shows an EZB holder from Six/Flipper, and page 50 shows an EZB not an IOTiny. Not sure why these pages are in the assembly instructions.
Thanks @Nink
Those two pages are correct for the following reasons:
The EZ-Robot LiPo battery comes shipped inside the Six body for added protection. It is a hard case for the battery and the battery needs to be removed once delivered to the customer.
In the IoTiny firmware the picture of the EZ-Bv4 was used for its webserver diagram. It was used during development at that time because the IoTiny final form factor didn’t exist yet. It’s one of those things that we forgot to go back and update. It’s hard to go back now and justify a firmware update to change a photo, so unfortunately it’s a classic case of "it is what it is".
*Edit Oops I forgot to mention that a build video is on the way! We’re putting the finishing touches on it.